|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Introduction
Cryptocurrency has revolutionized the world of finance and investment. One of the most intriguing aspects of this digital revolution is cryptocurrency mining. While mining was traditionally conducted using powerful hardware rigs, a new method known as cloud mining has emerged. In this blog, we’ll delve into the concept of cloud mining, its advantages, and potential risks, drawing insights from various sources, including Investopedia, Binance Academy, and Ledger Academy.
What is Cloud Mining?
Cloud mining is a method of cryptocurrency mining that doesn’t require miners to own and operate their own hardware. Instead, miners can lease computing power from a third-party provider that owns and maintains the necessary equipment in remote data centers. This remote mining setup allows individuals to participate in the cryptocurrency mining process without the need for technical expertise or substantial investments in hardware.
Aside from cloud mining, there are several other ways that cryptocurrency mining can be conducted:
Solo Mining
This is the original method of mining. In solo mining, a miner performs the mining operations independently, which requires a significant upfront investment in hardware depending on the cryptocurrency. If a block is successfully mined, the miner receives the entire block reward and transaction fees. However, because of the increased difficulty in mining cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, the chances of a solo miner successfully mining a block have decreased substantially.
Mining Pools
As mining got increasingly difficult, individual miners began pooling their computational resources to increase their chances of successfully mining a block.
This is called a mining pool. Miners in a pool share their hash power to solve the computational problem faster and when a block is mined, they split the reward based on the amount of computational power each contributed.
ASIC Mining
ASIC stands for Application-Specific Integrated Circuit. These are hardware systems specifically designed for mining certain cryptocurrencies. They are highly efficient but can be expensive and are often used in professional mining operations. They can be used in solo mining or in mining pools.
GPU/CPU Mining
Some cryptocurrencies can be mined with a regular CPU (Central Processing Unit) or GPU (Graphics Processing Unit). This was how Bitcoin mining initially started. However, as the difficulty increased, GPU and CPU mining have become largely inefficient for Bitcoin, but are still used for some other cryptocurrencies.
The effectiveness and profitability of these methods can vary greatly depending on the cryptocurrency, the hardware used, the cost of electricity, and the current network difficulty and other factors.
How Does Cloud Mining Work?
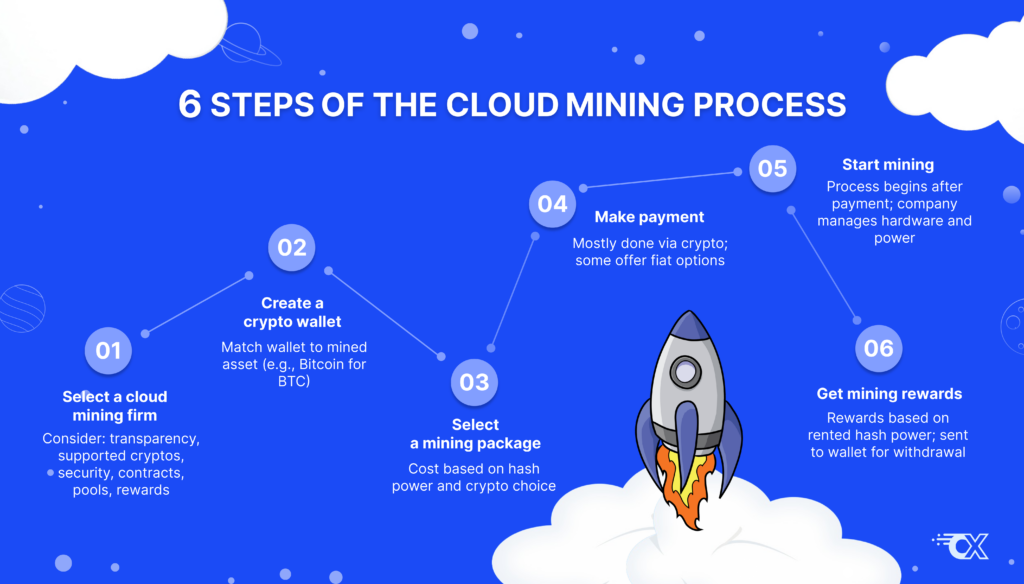
Cloud mining works by allowing individuals to rent or purchase a share of the computing power in a data center that is set up for mining cryptocurrencies.
This is how it typically works:
Step 1: Choose a cloud mining company
The first step is to choose a reputable cloud mining company. It’s important to conduct thorough and diligent research as there are unfortunately many scams in the cloud mining space.
Step 2: Select a mining package
Cloud mining providers often offer various packages based on how much computing power you want to rent and for how long. The more power you rent, the higher your potential returns. But this also comes at a higher cost.
Step 3: Choose a mining pool
Some cloud mining companies might also let you choose which mining pool you want to contribute to.
Step 4: Pay for the service
Once you’ve selected your package, you’ll need to pay for the service. This is typically done in cryptocurrency, although some services may accept fiat currency.
Step 5: Start mining
Once you’ve paid, the cloud mining service will set up the mining hardware, maintain it, and start the mining process. Your share of the processing power will be put to work to mine cryptocurrencies.
Step 6: Receive mining rewards
Rewards from the mining operation are shared among the users, according to how much of the total processing power they own. You’ll need to set up a wallet that’s compatible with the cryptocurrency you’re mining for this step.
Useful Metrics in Cloud Mining
When dealing with cloud mining, there are several important metrics to consider that can help you understand the potential profitability and feasibility of your cloud mining options.
Hash rate
The hash rate refers to the number of calculations a miner can perform in one second. Higher hash rates increase the probability of finding the next block in the blockchain and receiving rewards.
The hash rate is measured in hashes per second (H/s), but is typically represented in larger units like kilohash (KH/s), megahash (MH/s), gigahash (GH/s), terahash (TH/s), petahash (PH/s), and exahash (EH/s). Their definitions are as follows:
Energy consumption
Mining consumes a large amount of energy, which can be a significant cost for mining operations of all sizes. This is often measured in watts. The efficiency of a mining setup is often measured in joules per terahash (J/TH), which indicates how much energy the hardware uses to perform a certain amount of computation. Lower J/TH values are better, as this means the hardware is more efficient.
Cost per hash
This is the cost of your cloud mining contract divided by the total hash power you’re getting. It essentially tells you how much you’re paying for each unit of mining power. This can be useful for comparing different cloud mining contracts or companies.
Mining difficulty
Mining difficulty determines how hard it is to find the next block in the blockchain, and it changes over time depending on how many miners there are. Higher difficulty means you’ll need more hash power to mine the same amount of cryptocurrency.
Block reward
This is the amount of cryptocurrency you receive for mining a new block. It’s important to know this because it directly affects your potential earnings. Note that for some cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, the block reward halves every four years in an event called “halving.”
Price of cryptocurrency
This is the current market price of the cryptocurrency you’re mining. This is crucial because the profitability of mining is directly related to the price of the cryptocurrency you receive as a reward.
Pool fees
If you’re participating in a mining pool via your cloud mining contract, there will typically be a fee associated with that. This fee will reduce your earnings, so it’s important to know what it is.
Understanding these metrics can help you make an informed decision about whether or not to get involved in cloud mining, and which contract or company to choose if you do decide to participate.
Advantages of Cloud Mining
Accessibility:
Cloud mining democratizes access to cryptocurrency mining. It enables people with limited technical knowledge or resources to participate in the mining ecosystem. Anyone with an internet connection and a suitable cryptocurrency wallet can start cloud mining.
Cost-Efficiency:
Traditional mining rigs require a significant upfront investment in hardware, electricity, and cooling systems. Cloud mining eliminates these expenses, making it a cost-effective option for newcomers to the crypto mining space.
Maintenance-Free:
With cloud mining, users don’t need to worry about hardware maintenance, repairs, or upgrades. The cloud mining service provider handles all the technical aspects, ensuring smooth operation.
Diversification:
Cloud mining allows individuals to mine multiple cryptocurrencies simultaneously. This diversification can help spread risk and potentially increase mining profitability.
Accessibility to New Coins:
Cloud mining services often provide access to newly launched or less-known cryptocurrencies, allowing miners to explore different investment opportunities.
Potential Risks and Considerations
Scams and Fraud:
The cryptocurrency industry has its fair share of scams and fraudulent cloud mining services. It’s crucial to conduct thorough research and choose reputable providers to avoid falling victim to scams.
Lack of Control:
Cloud mining users relinquish control over their mining hardware, as it’s located in remote data centers. This lack of control means users are reliant on the provider’s honesty and performance.
Profitability Uncertainty:
Cloud mining profitability depends on various factors, including cryptocurrency prices, mining difficulty, and maintenance fees. Market fluctuations can impact returns significantly.
Limited Transparency:
Some cloud mining providers may lack transparency in their operations. It can be challenging to verify the legitimacy of their claims and the actual mining activities taking place.
Long-Term Viability:
The long-term viability of cloud mining depends on the duration of the mining contract and the cryptocurrency’s overall market conditions. It’s essential to consider whether the contract duration aligns with your investment goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cloud mining stands as a revolutionary force in the world of cryptocurrency mining, reshaping the landscape by eradicating numerous hurdles that have historically impeded aspiring miners. This innovative approach has democratized participation, making it accessible to a wider audience and also for its potential for cost-efficiency and portfolio diversification. However, it’s essential to approach cloud mining with caution due to the risks associated with scams, lack of control, and market volatility.
Ultimately, cloud mining holds immense potential for those seeking a more accessible and diversified entry into cryptocurrency mining, but success hinges on a blend of informed decision-making, risk management, and a keen awareness of the dynamic crypto landscape.