|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
In the evolving landscape of blockchain and cryptocurrency, governance tokens have emerged as a pivotal innovation, enabling decentralized decision-making within various blockchain projects. These tokens play a critical role in shaping the future of decentralized finance (DeFi) and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). But what exactly are governance tokens, and why are they important? Let’s dive in to understand their significance and functionality.
What are Governance Tokens?
Governance tokens are a type of cryptocurrency that grants holders certain rights and powers within a blockchain network or decentralized application (dApp). Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, which primarily function as a medium of exchange or store of value, governance tokens are designed to facilitate decentralized governance by allowing holders to participate in the decision-making processes of the project.
Key Features of Governance Tokens
Voting Rights: The primary function of governance tokens is to provide voting rights to their holders. Token holders can propose and vote on various aspects of the project’s development, including protocol upgrades, changes in governance structures, fund allocation, and other critical decisions.
Decentralized Control: Governance tokens help distribute control among the community members rather than a centralized entity. This democratization ensures that no single party has overarching control over the project’s direction, fostering a more transparent and fair ecosystem.
Incentivized Participation: By holding governance tokens, users have a vested interest in the success and sustainability of the project. This often encourages active participation and engagement from the community, leading to more robust and well-considered decisions.
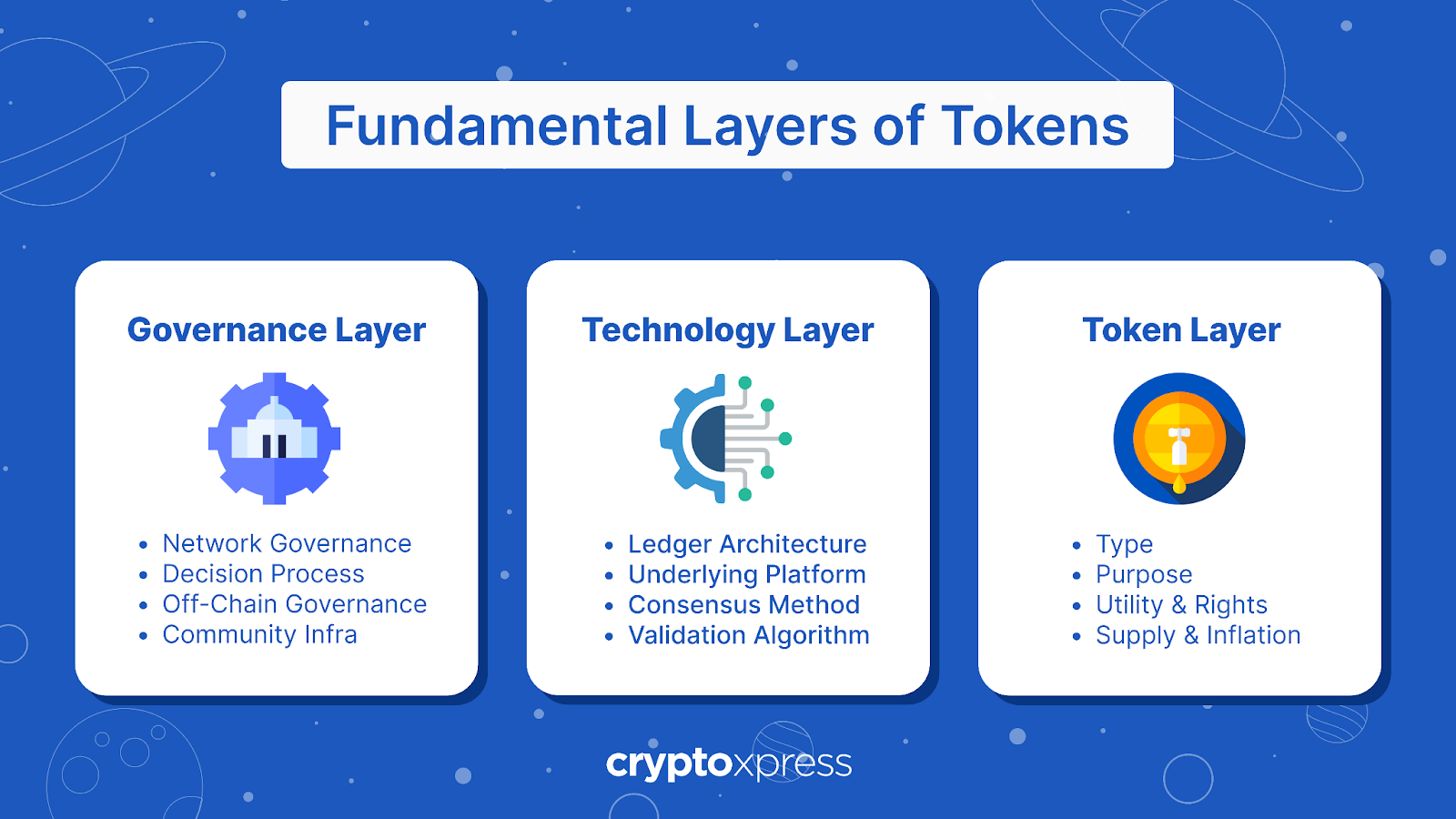
How Do Governance Tokens Work?
Governance tokens operate on the principle of decentralized consensus. Here’s a step-by-step overview of how they typically function:
Proposal Creation: Any token holder can create a proposal outlining a change or improvement they wish to implement within the project. This could range from technical upgrades to alterations in the project’s strategic direction.
Voting Period: Once a proposal is submitted, it enters a voting period where all token holders can cast their votes. The weight of each vote is usually proportional to the number of tokens held, meaning those with more tokens have a greater influence on the outcome.
Execution: If a proposal receives the required number of votes and meets any predefined conditions, it is approved and implemented by the project’s development team or automated smart contracts, depending on the governance structure in place.
Examples of Governance Tokens
Maker (MKR): MakerDAO, a decentralized lending platform, uses the MKR token for governance. MKR holders can vote on critical issues such as risk parameters and the types of collateral accepted by the platform.
Compound (COMP): The Compound protocol, a popular DeFi lending platform, employs COMP tokens for governance. COMP holders can propose and vote on changes to the protocol, including interest rate models and collateral factors.
Uniswap (UNI): Uniswap, a decentralized exchange, uses UNI tokens to allow holders to participate in the governance of the protocol. UNI holders can vote on proposals related to fee structures, token listings, and more.
The Importance of Governance Tokens
Governance tokens are crucial for the sustainability and growth of decentralized projects. They provide a mechanism for the community to actively participate in the evolution of the project, ensuring that the interests of the majority are considered. This decentralized approach to decision-making helps avoid the pitfalls of centralized control, such as single points of failure, and promotes a more resilient and inclusive ecosystem.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While governance tokens offer numerous benefits, they also come with challenges. For instance, the concentration of tokens among a few holders can lead to centralization of power, undermining the democratic ethos of decentralized governance. Additionally, voter apathy can result in low participation rates, impacting the effectiveness of the governance process.
Looking ahead, the evolution of governance token models will likely focus on addressing these challenges. Innovations such as quadratic voting, where the cost of each additional vote increases exponentially, can help mitigate the influence of large token holders. Moreover, incentivizing participation through rewards or staking mechanisms can encourage more active involvement from the community.
Conclusion
Governance tokens represent a significant advancement in the realm of blockchain and decentralized technologies. By empowering token holders with voting rights and decision-making power, they foster a more inclusive and democratic ecosystem. As the DeFi and DAO landscapes continue to evolve, governance tokens will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of decentralized projects. For investors, developers, and enthusiasts, understanding and engaging with governance tokens is essential to participate in the exciting journey towards a more decentralized world.